Stuck or Non-Responsive Process
How to kill a process from cmd
To kill a process from the command line, we will use the taskkill command. This command is available in Windows XP and later versions of Windows.
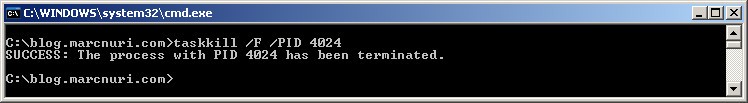
If you know the process ID (PID), you can use the following command:
taskkill /F /PID <pid>For example, consider that we need to kill a process that is blocking a TCP port. We’ve retrieved its PID using the netstat command as I explained in the previous post. The PID is 4027, so we can kill it using the following command:
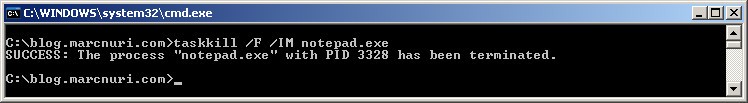
Taskkill also supports killing a process by its name. To do so, you can use the following command:
taskkill /F /IM <process name>For example, to kill all the notepad.exe processes, you can use the following command:
How to kill a process from PowerShell
To kill a process from PowerShell, we will use the Stop-Process cmdlet.
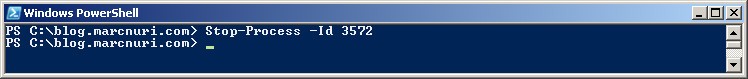
Just like with taskkill, if you know the process ID (PID), you can use the following command:
Stop-Process -Force -Id <pid>For example, to kill the process with PID 3572, you can use the following command:
In addition to the long format, Stop-Process has two other aliases that you can use instead: kill and spps.
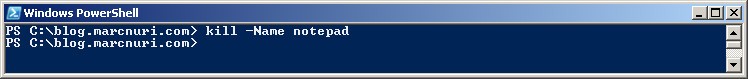
We can also kill a process by its name. To do so, you can use the following command:
Stop-Process -Name <process name>For example, to kill the Notepad process, you can use the following command: